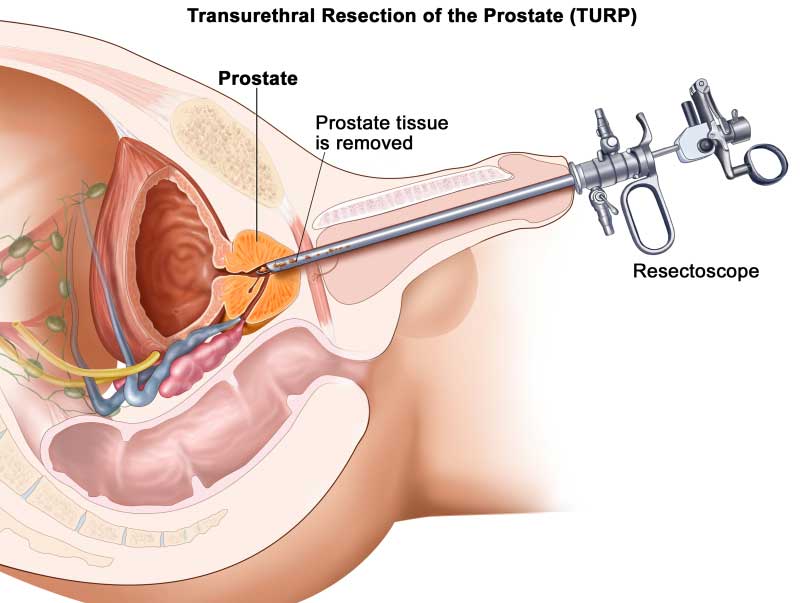
TURP has been a common procedure for enlarged prostate for many years, and it is the surgery with which other treatments are compared. With TURP, a surgeon places a special lighted scope (resectoscope) into your urethra and uses small cutting tools to remove all but the outer part of the prostate (prostate resection). TURP generally relieves symptoms quickly, and most men have a stronger urine flow soon after the procedure. Following TURP, there is risk of bleeding and infection, and you may temporarily require a catheter to drain your bladder after the procedure. You'll be able to do only light activity until you're healed.
TURP required the doctor to insert a device up the urinary tube and remove the prostate, as pieces at a time. This procedure was found to be effective at stopping the symptoms. But there were complications from this type of procedure. Such as erectile dysfunction, blood in the urine, blood loss even few days after surgery, water intoxication and urinary incontinence. Also TURP could only be performed on prostates that are 60 cubic centimeters in size or less. This type of surgery is generally done if you have a very large prostate, bladder damage or other complicating factors, such as bladder stones. It's called open because the surgeon makes an incision in your lower abdomen to reach the prostate. Open prostatectomy is the most effective treatment for men with severe prostate enlargement, but it has a high risk of side effects and complications. It generally requires a short stay in the hospital and is associated with a higher risk of needing a blood transfusion.
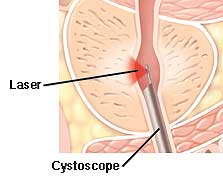
Laser surgeries (also called laser therapies) use high-energy lasers to destroy or remove overgrown prostate tissue. Laser surgeries generally relieve symptoms right away and have a lower risk of side effects than does TURP. Some laser surgeries can be used in men who shouldn't have other prostate procedures because they take blood-thinning medications.
Any type of prostate surgery can cause side effects, such as semen flowing backward into the bladder instead of out through the penis during ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation), loss of bladder control (incontinence) and impotence (erectile dysfunction).